Test Driven Development
by Srinesh Nisala (Senior Software Engineer @ iLabs)
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/srinesh-nisala/
- GitHub: https://github.com/s1n7ax
Pre-requisites
- Create a Github account
- Get a fork of https://github.com/s1n7ax/lecture-tdd
- Open the project with Codespace
Project structure
- Explain how to run the application using IDE & Gradle
# with gradle
gradle run
# with gradle wrapper
./gradlew run
- Explain how to run tests using IDE & Gradle
# with gradle
gradle test
# with gradle wrapper
./gradlew test
Basics of JUnit
-
Create a simple test to print hello world (check the output in the debug console tab)
-
Introduce
beforeEachandafterEachannotations
Exercise 1
- Create a
Calculatorclass and addadditionmethod - Show how to use IDE features to quickly create a test class
- Tryout the
additionmethod manually - Create a unit test to test the
additionmethod
Exercise 2
- Create a test case for
subtractionmethod - Use IDE features to generate the method signature
- Implement the
subtractionmethod
What is TDD?
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a Software development method in which you write Automation Tests before the actual development process starts
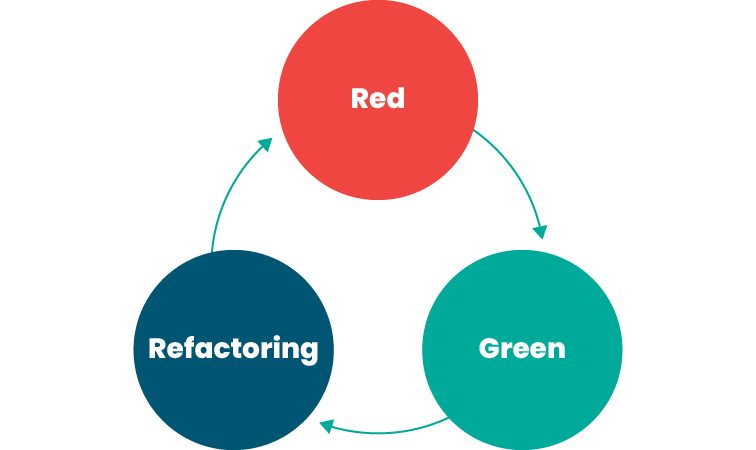
Red-Green-Refactor:
- Focus on testing behaviors (requirements) rather than implementation details.
- Write minimal code to pass tests ("green"),
- Refactor without adding new tests.
TDD Best Practices
- Reduce mocking and stubbing
- Avoid testing private/internal code; focus on public interfaces
- Avoid Over-Testing